What Is The Difference Between Insulation Types THHM And THWN? Each jacket has information printed on it to help you choose the correct product for your job.
A letter code provides the attributes of the wire, along with material, gauge and voltage rating.
When planning on running the wiring for a building, you’re probably wondering which wire to use.
This article discusses in-depth building wires, THHM vs. THWN, to help you understand the choices you’ll need to make.
What Are A Building Wires and Cables?
Building cables and wires convey electrical current from a power source to a device, such as a lighting fixture or outlet, running through raceways, cable trays, or conduits.
Users employ them to extend old circuits or run new circuits inside ceilings and walls in residential, industrial, and commercial settings.
Building Wire Construction:
Insulation: PVC (Poly Vinyl Chloride) with Secondary Nylon Jacket
Voltage Rating: 600 Volts.
Conductor: Annealed solid or stranded copper wires (copper or CCA)
It’s vital to correctly size and install the building cable and wire to keep the electricity running.
The different categories include all the types recognized by the NEC, CSA Standards, ANCE Standards, Mexican Electric Code, and the Underwriters Laboratories.
The NEC has a letter system to help you easily identify a wire’s capabilities. Some of the common letters include THHN, THWN etc.
Below are the attributes and letters commonly found in residential wiring;
- X – flame retardant, synthetic polymer
- HH – high heat resistance
- N – gas and oil resistant, nylon coating
- T – thermoplastic insulation
- H – heat resistant
- W – ideal for wet conditions

Caption: Cable Trays
Below are the various types of building wires.
TW/THW Building Wire
TW/THW ( thermoplastic high heat-resistant and water-resistant) wire is basically a coated wire run through feeder and branch circuits, building wiring, and internal secondary industrial distribution control panels, including refrigeration equipment, control wiring of machine tools, air conditioning equipment, and automatic washers.
This tracer wire is ideal for residential, commercial, and industrial settings where it is wet or dry and less than 75°C/194 F.
THHN Building Wire
THHN (Thermoplastic High Heat Resistant Nylon) building wires run through cable trays or conduits.
This wire normally supplies electric current in various indoor wiring projects, including appliances and closed circuits.
It features a durable nylon jacket resistant to abrasion, shields the metal conductor and thermoplastic insulation from damage, and protects against shock.
THHN is the best choice for transmitting high loads of electric current (up to 600V) in industrial and commercial settings.
It can withstand temperatures of up to 900C for prolonged periods. If you plan on burying it, place it in a conduit.
THWN Building Wire
THWN (Thermoplastic heat- and water-resistant nylon) is ideal for industrial and commercial settings because it can conduct up to 600V of electric current.
It’s durable and resistant to oil and water and can work in wet conditions for prolonged periods without decreasing performance.
Also, it can withstand temperatures of up to 900C.
What Is The Difference Between Insulation Types THHM And THWN: TFFN Fixture Wire
TFFN (Thermoplastic Flexible Nylon) wire is a coated wire run through raceways Compared to THHN, TFFN is more flexible but offers less heat resistance and is available in a limited number of gauges (16 AWG and 18 AWG).
The TFFN is ideal for machine tool wiring, appliances, control circuits, and power-hardwired light fixtures in walls and ceilings for commercial applications.
Its stranded conductor increases flexibility and is easily attachable to other surfaces.
It can withstand temperatures of up to 900C in dry and 600C in wet conditions.
Also, it is oil resistant, making it ideal for both outdoor and indoor applications.
What Is The Difference Between Insulation Types THHM And THWN: XHHW Building Wire
XHHW (Cross-linked Polythene High Heat Resistant Water Resistant) building wire is basically a coated wire run through raceways.
Its thick jacket offers better protection than the THHN wire, making it highly resistant to abrasions, ozone, and chemicals.
Its cross-linked polythene is more flexible than THHN’s thermoplastic insulation, enabling it to flex and bend more easily, making it a choice for projects that need close-spaced and complex bends.
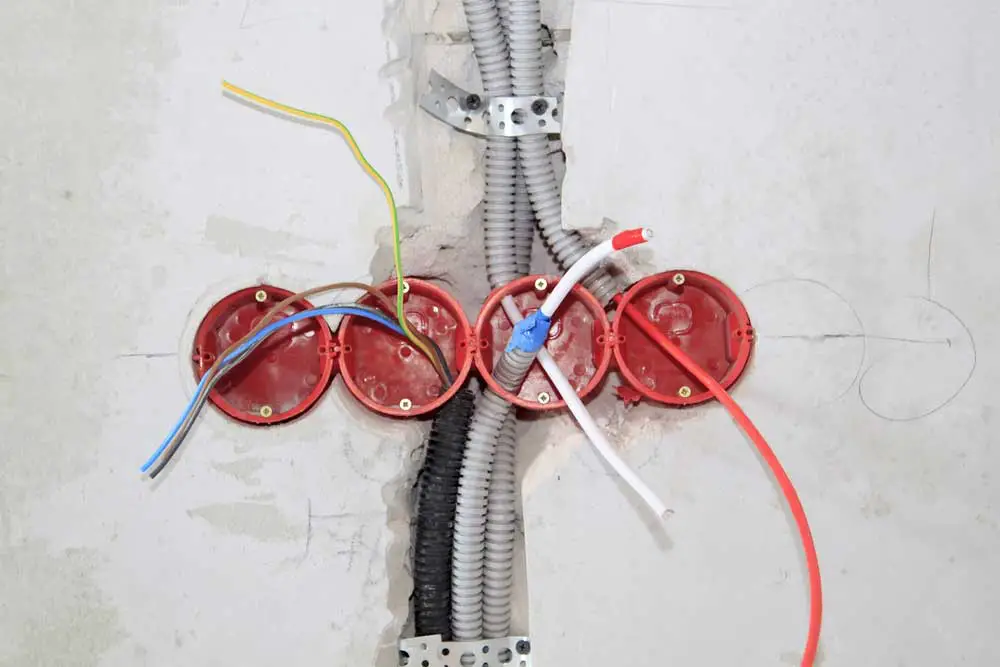
Caption: Wiring in the wall
What Is The Difference Between Insulation Types THHN And THWN: Choice
| THHN | THWN | |
| Similarites | conduct up to 600 volts;water-resistant; withstand temperatures up to 90 degrees Celsius;Insulation: PVC (Poly Vinyl Chloride) with Secondary Nylon Jacket;Conductor: Annealed solid or stranded copper wires (copper or CCA);both suitable for industrial settings;Wire color code:Standard wire color codes make it easier for the next person working on the wiring to know their way around it. Red – hot wire for connecting hardwired smoke detectors and switch legs.Black – hot wire for outlets and switches.Green and Bare Copper – grounding purposes only.White – neutral (sometimes marked with red or black to indicate no longer neutral).Yellow and Blue – hot wires pulled through conduit. Yellow is ideal for lights and switch legs, while blue is ideal for three-way switch applications. | |
| Differences | better at resisting high temperatures for a long time/have heavy electrical loads that produce a lot of heat.Wet climates will affect its performance/maximum performance in dry climates. | better at resisting moisture and exposing to water for a long time won’t affect its performance . |
| Thinner and more fragile, meaning you should run it through a conduit. | Thicker and more durable, meaning you can use it for both indoor and outdoor settings. | |
Conclusion
So what is the difference between insulation types THHM and THWM? We hope you can now distinguish between the two.
All the necessary information has been laid out above to help you make the right choices when deciding on the wiring.
If you have any issues or queries, feel free to contact Cloom Tech.
