With various important elements to consider, we will discuss some of the different automotive wire insulations available today and how to use them to protect your wires and cables.
As the link between the engine compartment and the fuse block or starter, automotive wires and cables are an integral part of the electronic makeup of a vehicle and how it functions.
Whenever a faulty connection occurs, the battery or engine compartments can cease functioning, leading to poor performance and presenting various safety hazards.
What Is Automotive Wire Insulation?
Automotive Wire insulation refers to the non-conductive material in a cable’s construction.
One of the primary functions is to resist electrical leakage, which is basically about preventing the wire’s current from coming into contact with others or the cables nearby.
It also plays a critical role in preserving the material integrity of the wire by protecting it against various environmental threats, such as heat and water.
So, it is important to note that the effectiveness or longevity of a wire greatly depends on its insulation.
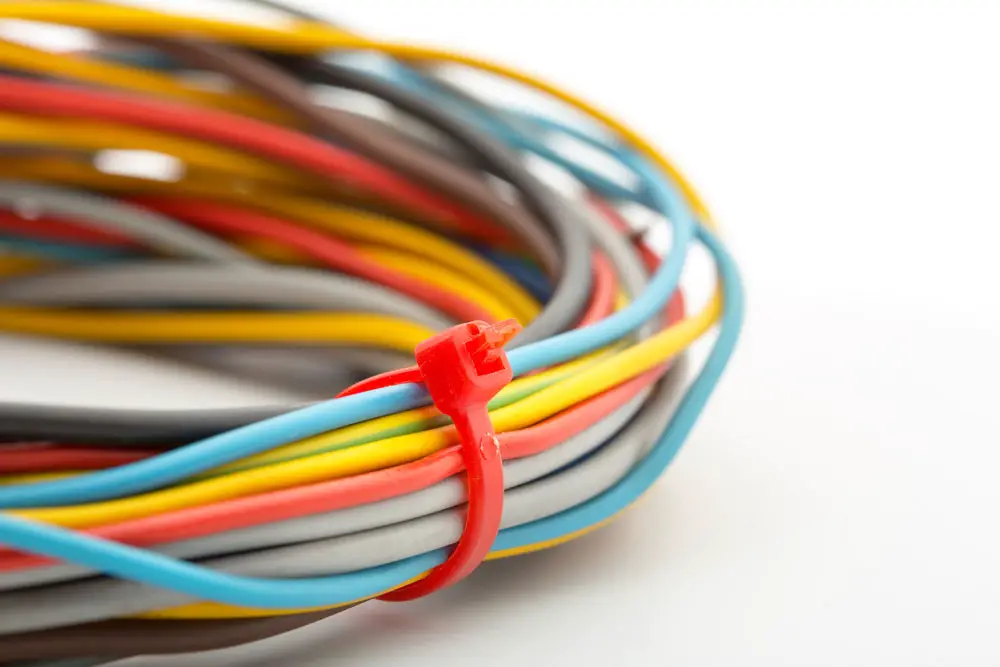

Bundled Wires
The Evolution Of Automotive Wire Insulation
You can use PVC-insulated wires rated to withstand 80° Celsius to 105° C in most areas of a race car or hot rod, except the engine.
There is also Teflon that can withstand temperature ranges of 400 to 500° F.
When you consider that the engine compartment can reach temperatures of around 300° F and then add the chemical mix commonly found in cars, you can understand why the insulator tends to deteriorate quickly.
One possible answer to the problem could be Tefzel, which is closely associated with Teflon, but the military grade.
Despite not having the same heat resistance as the latter, it offers more abrasion capabilities.
Tefzel is also generally available in various gauge sizes and can be purchased at aircraft avionics shops.
Car electrical system
Low-Voltage Automotive Wires And Their Insulation
Below are the two main types of automotive wires and their insulation.
GPT Wire
General Purpose Thermoplastic (GPT) is a general circuit wire for basic vehicle applications.
Manufacturers create it by heating PVC insulation, which is then extruded through a die and placed onto bare copper.
This framework allows it to accommodate as much as 60 V and withstand different temperature ranges from -45°C to +85°C.
More affordable than cross-link, you can see the GPT wire in under-the-hood scenarios or in-the-cabin applications.
However, its liquid and heat resistance features are not as good as those of cross-link wire.
As a result, you cannot use GPT wire near the engine compartment or in areas exposed to the elements or liquids.
Cross-Link Wire
Unlike the GPT wire, Cross-link wire, well-suited for intensive conditions, is an automotive wire with better durability features.
It is rated at -51°C to +125°C, resisting grease, moisture, oil, most acids, and gasoline.
However, it comes at a higher price.
Manufacturers make it by extruding the relevant material via a tube, using immense pressure and heat to cross-link/alter the molecules responsible for insulation to create another type of state.
Some of the primary applications of cross-link wire include heavy or intense-duty industries that require wire capable of taking a beating, like the fuse blocks found inside engine blocks or in electrical setups that are most likely to get exposed to air or other environmental elements.
In addition, it is usually preferred over GPT wire for applications that must adhere to SAE regulations.
Regarding cross-link wire, there are generally three categories based on wall thickness and insulation. Nonetheless, all of them are great for automotive applications requiring high efficiency and reliability in extremely hot or cold environments.
- SXL insulation, ideal for under-the-car usage or exposed areas, is the thickest and offers the best abrasion resistance.
- GXL insulation tends to be resilient enough for application under-the-hood usage, including engine compartments of trailers and trucks. But it is thinner than the SXL, which means its light, flexible, and more affordable than its SXL counterpart.
- TXL insulation is thinner than its GXL counterpart but still durable for under-the-hood usage. Some primary benefits of TXL insulation include flexibility, easy usage, compact nature, and the ability to slide into tightly packed compartments.
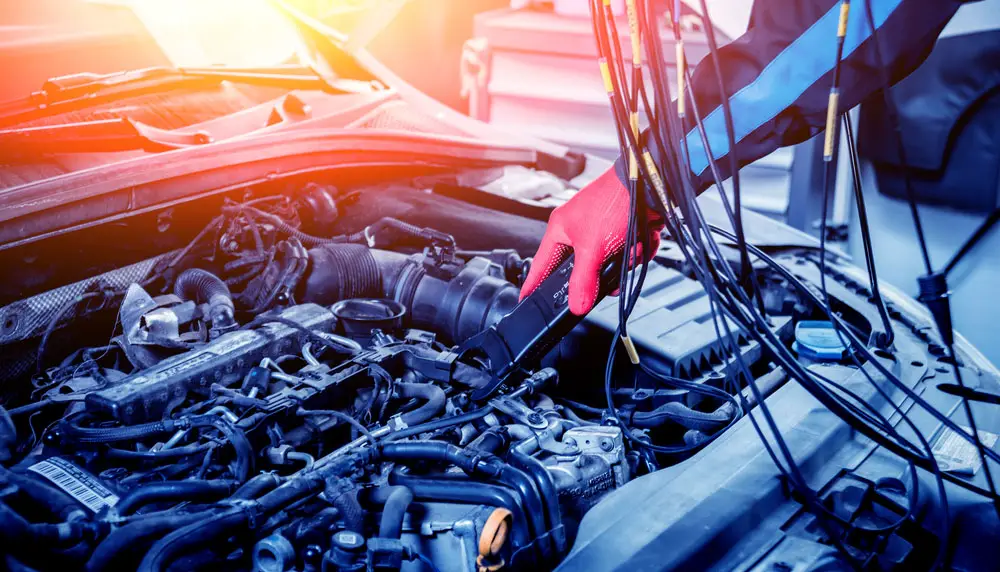

Wire harnesses and cable assemblies under the hood
High-Voltage Automotive Cables And Their Insulation
These high-voltage (around 600 V) cables facilitate connections between the generator, inverter, converter, and batteries found in hybrid, fuel cells, and all-electric vehicles.
SGT Battery Cable
It is a common battery cable used for various applications, including battery replacements and car projects.
Viewed as a friendlier option for general jobs, its PVC insulation is strong enough to get the job done but lacks the additional features of the SGX battery cable.
SGX Battery Cable
It’s considered among the ideal options for battery cables because it provides users with an adequate heat protection rating of 125°C/257°F.
Also, it comes with different kinds of insulations made of XLPE, which make it a great choice for those looking for a wire that can resist things like steering fluid and everything in between.
It offers additional protection; you can apply it in the engine compartments of cars, boats, RVs, buses, and trucks.
Finally, the SGX, known to be reliable and durable, has the only major drawback is its costly price tag.
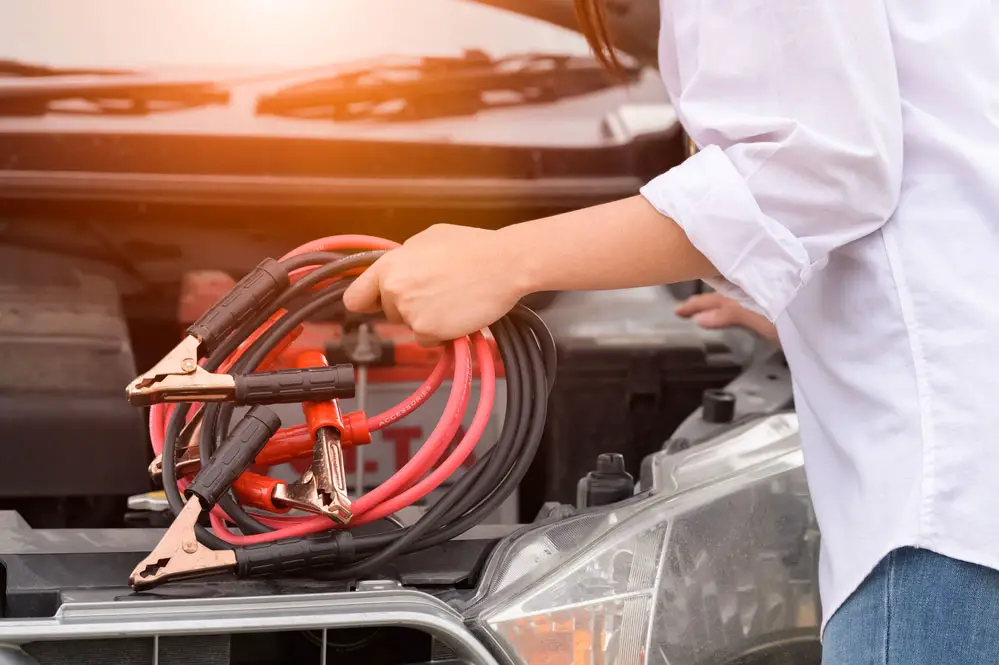

Hand-holding battery cables
Conclusion
High-performance and efficient wires and cables can adhere to the strained power requirements, maintain stable properties, and allow for easy installation processes, particularly in complex harnesses.
For all your automotive wire harness needs, contact Cloom Tech.
